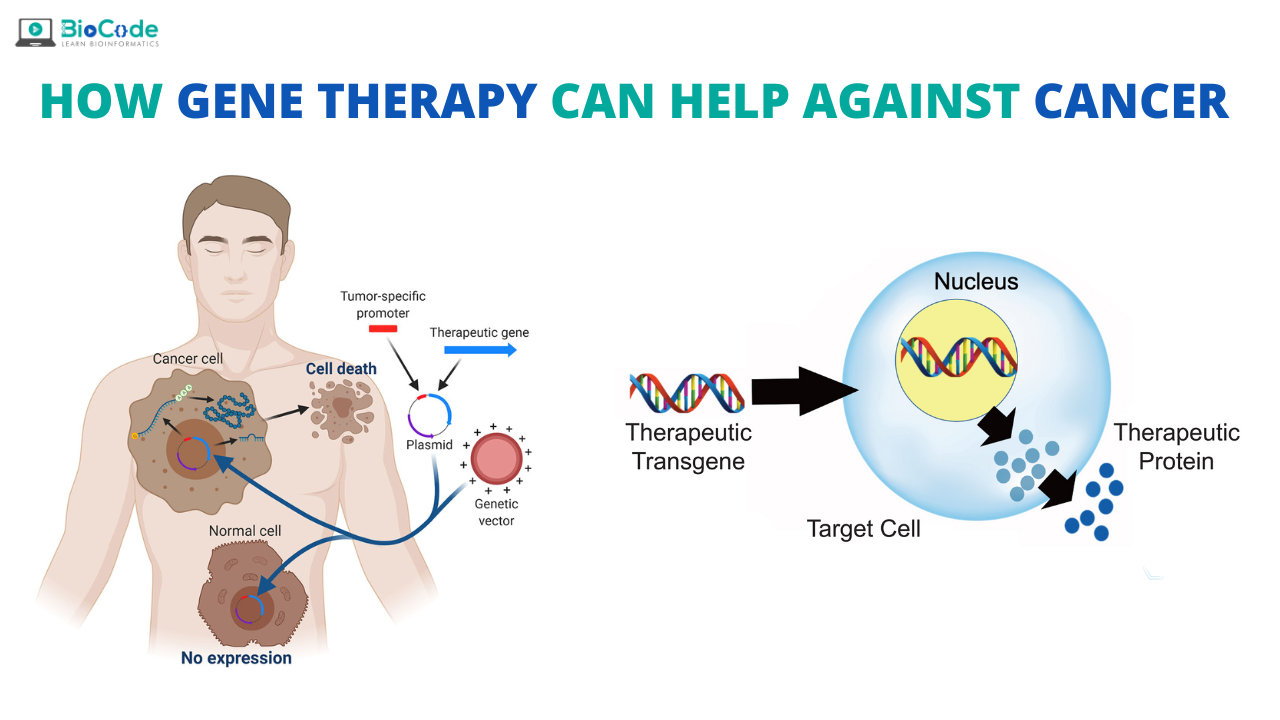
If a gene becomes disrupted, this disruption is called a mutation. This disruption can lead to a gene not working properly and abnormal cell growth. When a cell either grows uncontrollably or too quickly, it can cause cancer in the body. Developing a cancer is not as simple as this in fact it requires a complex series of multiple mutations. Mutation in the genes can be caused by various factors for instance smoking, environment, or inheritance.
Gene Therapy
In order to repair the mutations caused in the genes, gene therapy is used. Gene therapy is a way of treating or preventing a disease by modifying the genetic instructions within an individual’s cells. In gene therapy we are basically inserting foreign genetic material into the diseased host tissue to alter the expression of a gene product or to change the biological properties of cells for therapeutic use.
Genes are responsible for all the aspects of cell life. Genes hold the code for proteins that enable cells to grow, function and divide. When a gene is defective, it can cause the protein to malfunction or to not be produced at all. When a gene is absent, or is overactive, important bodily functions may be impaired or disabled. The goal of gene therapy is to correct such gene problems by fixing them at the source.
Gene therapy can involve replacing abnormal or missing genes with healthy ones that enable cells to produce useful proteins. Gene therapy may involve changing the way genes are regulated, so that abnormal (under or overactive) genes operate properly. Finally, gene therapy can be used to express entirely foreign genes in cells that change their function and/or survival.
Gene Therapy Treatments & Research
There are various different attempts and efforts underway to apply gene therapy in cancer treatments. Most of these efforts are in early, experimental stages, where they’re being studied in the laboratory or in clinical research trials. One approach, however, known as CAR T-cell therapy, in which T cells are genetically engineered to produce an artificial T cell receptor to fight cancer cells has received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use as a therapy in certain groups of patients and is expected to receive additional approvals in the near future.
Research in gene therapy for cancer is currently focused in multiple areas including gene transfer to alter the abnormal functioning of cancer cells, genetically engineered viruses that directly kill cancer cells and immunotherapy which includes CAR T-cell therapy as shown in the figure below. CAR T-cell therapy helps the immune system to find and kill tumor cells. Similarly, CRISPR/Cas9 is also used for gene therapy. It is a simple two-component system used for effective targeted gene editing as shown in the figure.
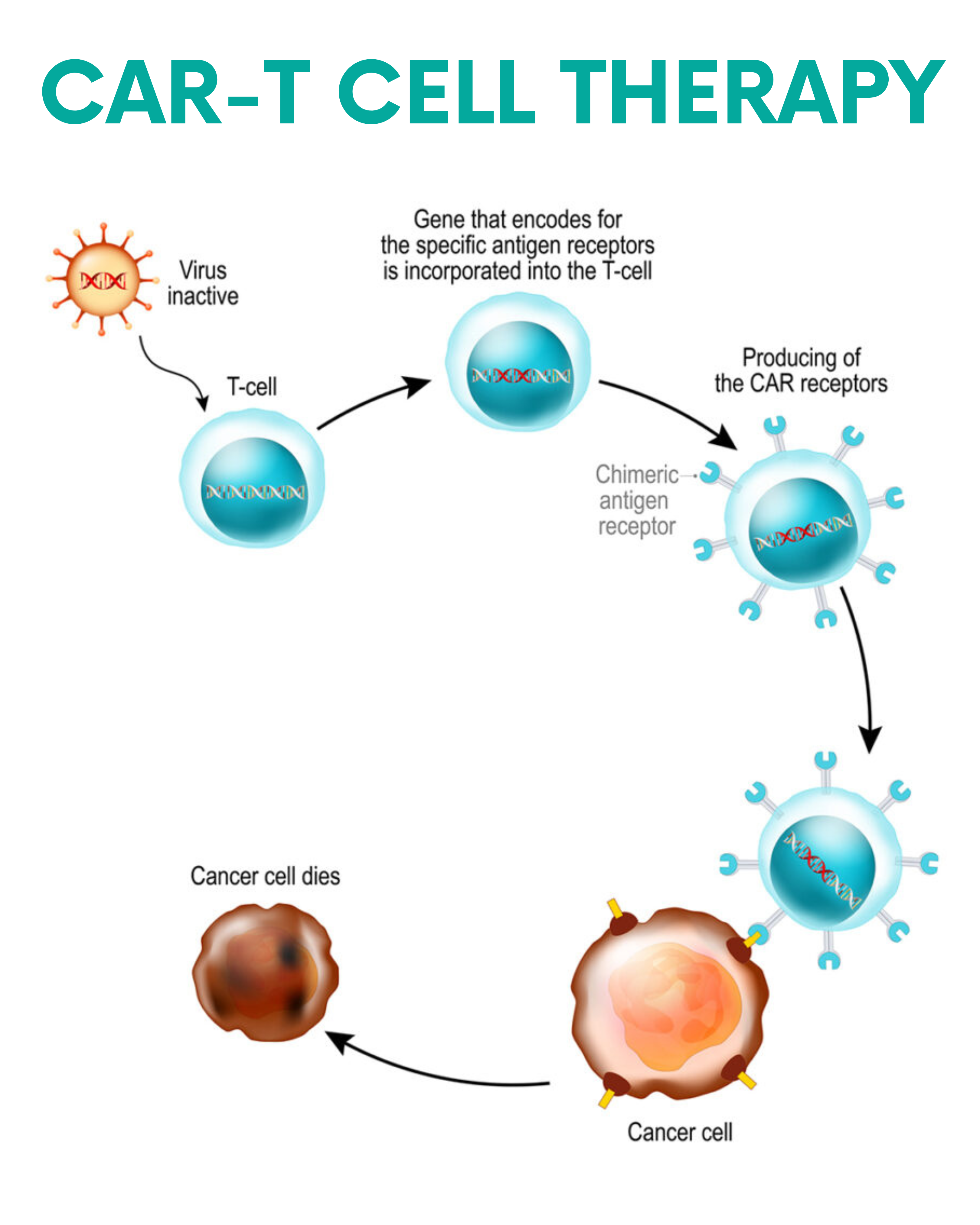
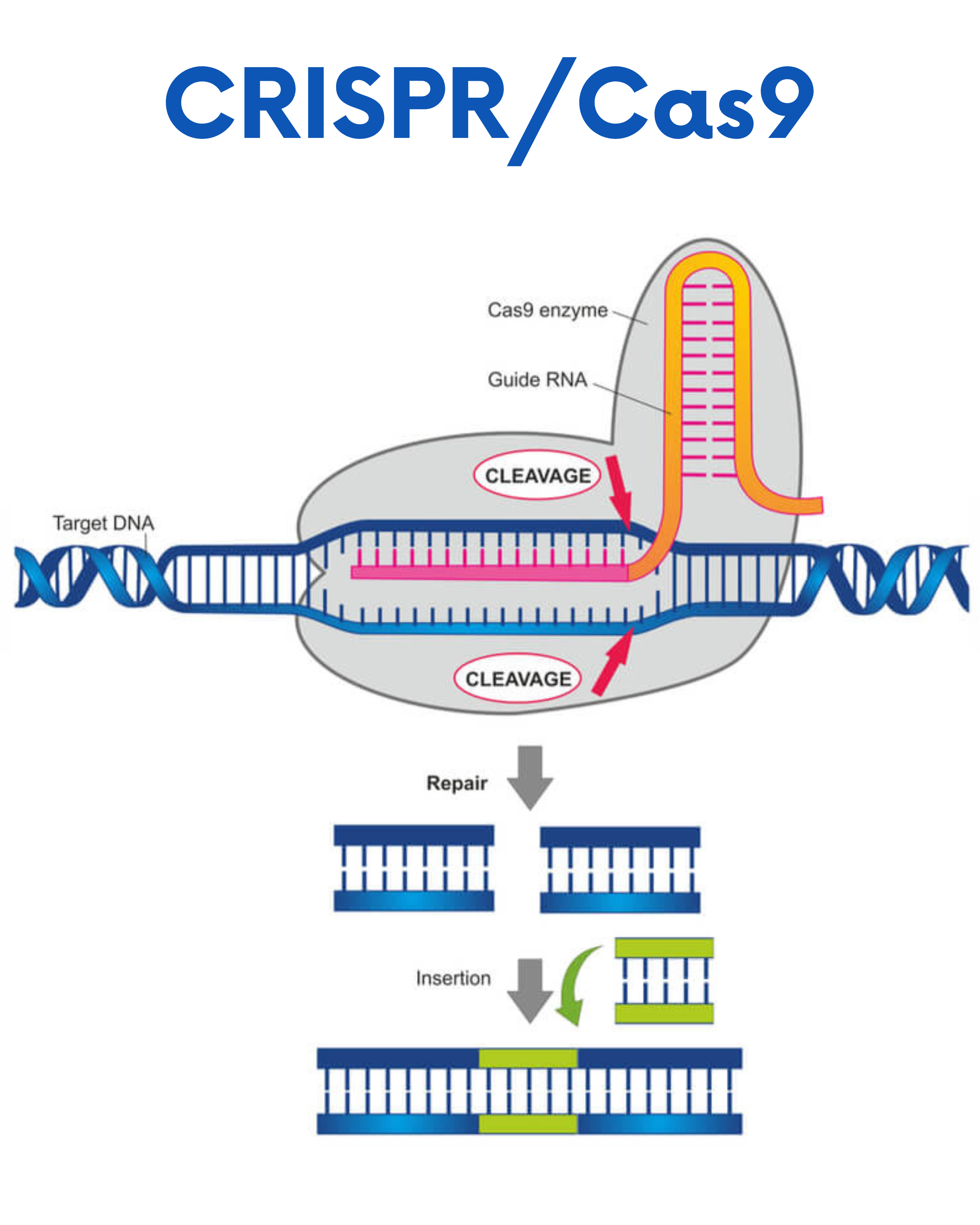
Role of Bioinformatics in Cancer Gene Therapy
Cancer bioinformatics deals with organizing and analyzing the genomic data to identify the important trends and patterns. With the help of bioinformatics, it has become easier to distinguish the specific gene and protein targets on which the cancer cells depend on. This helps in directing the therapeutic agents against the identified targets. Furthermore, the occurrence of genetic variation between the same tumor type in different individuals that can affect the disease progression or response to therapy is also identified with the help of bioinformatics. Bioinformatics plays an important role in genome-based therapies by collecting information on all of the human genes and proteins.